CONTAIN:
1.
INTRODUCTION
2.
SYSTEM OF UNITS (MEASUREMENT).
3.
DIMENSION.
4.
UNIT AND DIMENTION
5.
SIGNIFICANT FIGURE
DESCRIPTIVE PART
†1: What is PHYSICS?
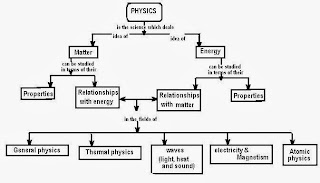
The word 'Physics' comes from the Greek word 'phusis' meaning 'nature', introduced by the ancient scientist 'Aristotle'. Man has always been fascinated by nature. The branch of science which is devoted to the study of nature and natural phenomena is called Physics. It is expected that all the events in nature take place according to some basic laws. Thus Physics (the knowledge of nature) is the science concerned with the discovery and understanding of the most basic fundamental laws of the universe that control the way everything in the world around us behaves. Discoveries in basic physics have important ramifications for all of science.
Physics is the scientific study of matter and energy and how they interact with each other. Physics deals with matter on scales ranging from sub-atomic particles (i.e. the particles that make up the atom and the particles that make up those particles) to stars and even entire galaxies. Physics is the truly universal science.
There are many fields of physics, for example: mechanics, electricity, heat, sound, light, condensed matter, atomic physics, nuclear physics, and elementary particle physics. Physics is the foundation of all the physical sciences, such as chemistry, material science, and geology and is important for many other fields: biology, medicine, computing, ice hockey, and television, list goes on.
The physics was divided in main two branches: i. Classical mechanics ii. Quantum mechanics.
The Mechanics or classical physics is an important field of physics. Developed by Sir Isaac Newton in the 17th century, the laws of mechanics and the law of gravity successfully explained the orbits of the moon around the earth and the planets around the sun. Newton’s laws are used to design cars, clocks, airplanes, earth satellites, bridges, buildings, just about everything, it seems, except electronics.
Electricity is another example of physics, one that you may experience as a spark when you touch a doorknob on a dry winter day. The electrical attraction of protons and electrons is the basis for chemistry. Magnetism is another force of nature, familiar to us from refrigerator magnets and compasses. In the 19th century, James Clerk Maxwell combined electricity and magnetism. He showed that light is an electromagnetic wave that travels through empty space.